
BBTC Ltd. – Stock Analysis (2024-25)
In this article we will try to analyze Bombay Burmah Trading Corporation Ltd. based on previous six years of financial statements viz Balance sheet, Profit and Loss statement and Cash flow statement. With this fundamental analysis we will try to gain insight into the business activities, financial health, operating efficiency and profitability of the company and finally try to derive the intrinsic value of the stock using Discounted Cash Flow method and the price at which the stock becomes attractive for long term investment. This article is divided in three sections as listed below :-
Section 1: Qualitative Fundamental Analysis comprising of General Introduction, Business overview dwelling into Business Model, Strengths and Weakness, Long Term Sustainability and finally the competitors.
Section 2:Quantitative Fundamental Analysis on Financial Health, Operating Efficiency And Profitability.
Section 3: Calculation Of Intrinsic Value.
General Introduction
Dated: 28 Mar 25
Company: Bombay Burmah Trading Corporation Ltd.
CMP: Rs. 1,729.35
Market Capitalisation: Rs. 12,363.23 Cr.
Share Holding Pattern:
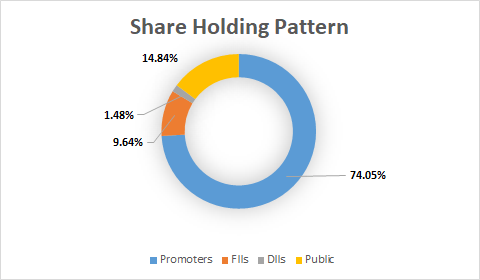
Promoters: Nusli N Wadia, Ness N Wadia
Peers: Samvardhana Motherson International, Bosch, Uno Minda, Exide Industries
****************************************************
Fundamental Analysis Of Bombay Burmah Trading Corporation Ltd.
Qualitative Analysis
General Introduction:
BBTC was set up about 150 years back in 1863 as a tea trading company between Bombay and Burmah and today is a Wadia Group Enterprise. The company is among one of the most eminent and reputed manufacturers and exporters of naturally grown Organic Tea and produces over 8 million kgs of tea annually. The company also holds majority stakes in Britania Industries which is also a part of the Wadia Group Company. The company has interests in Tea Estates, Auto Electric Components and Dental products manufacturing.
Business Overview:
The Company Operates three verticals viz. Tea & Coffee cultivation and production, Auto electric components manufacture and Dental products manufacturing.
Tea & Coffee Business:
In this the company produces normal tea as well as green tea. It also purchases tea leaf from other plantations to produce final product. It operates three estates in Tamilnadu, India – Mudis Group, Singampatti Group and Dunsandle Estate in the districts of Coimbatore, Thirunalveli and Nilgiri. India and China account for 64% of total global demand of tea.
The company has sold off its plantations in Tanzania since it was becoming more and more uneconomical to sustain due to the dropping production and sales. Further, the company has fully divested from Coffee business and used the proceeds to reduce long term debt.
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the tea plantations company appears promising, driven by strategic initiatives aimed at enhancing efficiency, quality, and profitability. The company benefits from a well-diversified portfolio that includes both conventional and organic tea, catering to a wide range of markets. This diversification helps optimize sales averages while reducing dependence on limited sales channels. Additionally, there is significant scope to improve the harvesting cycle through mechanization and the deployment of additional workforce, ensuring better productivity. Investments in factory automation are expected to lower costs while enhancing product safety and quality. To further improve yield and plant density, the company plans to replace aging tea plants with new, high-yielding varieties. Moreover, a large-scale expansion into retail tea sales and premiumization various varieties of tea is set to strengthen the bottom line by increasing the average selling price. Collectively, these initiatives along with the rising income levels and increasing population size position the company for sustainable growth and improved profitability in the coming years.
Areas of Concern:
The tea plantations company faces several threats, risks, and concerns that could impact its future performance. As an agricultural enterprise, it is highly vulnerable to unpredictable and unseasonal weather, which disrupts production schedules. Climate change is also influencing pest and disease outbreaks, with the Tea Mosquito Bug alone capable of causing up to 25% crop loss within just a couple of months. Additionally, an aging workforce and labor shortages are putting pressure on field operations, affecting productivity and quality. The mandatory three-year wage settlement for plantation workers further adds financial strain, increasing wages by 20-30% without a direct correlation to productivity or profitability improvements. Market challenges persist as well, with stagnant domestic auction prices and sluggish private sales growth over the past six years, except for FY 2020-21. Compounding these issues, the withdrawal of orthodox tea production and export subsidies by the Tea Board has reduced potential returns and incentives for export. Furthermore, the ongoing shortage of fertilizers—partly due to the Ukraine war and changes in government subsidy policies—has led to a 100% rise in Potash fertilizer costs, further increasing input expenses. These challenges underscore the need for strategic adaptation to mitigate risks and sustain long-term profitability.
Auto Electrical Components Business:
India’s fast GDP growth, coupled with rising incomes, boost in infrastructure spending and increased manufacturing incentives, has accelerated the automobile industry. Significant demand for automobiles also led to the emergence of more original equipment and auto components manufacturers. The auto components industry accounted for 2.3% of India’s GDP and provided direct employment to 1.5 million people. By 2026, the automobile component sector will contribute 5-7% of India’s GDP.
This division has been in business for over three decades and has four manufacturing facilities in Chennai and is a preferred supplier of leading Automotive OEMs. The company manufactures switches, solenoids, sensors, slip rings, and other plastic molded parts for the automotive application for both passengers and commercial vehicles and two wheeler segment.
The major customers of the company include Bosch, Wabco, TVS, NCR, Hero Moto Corp, TVS Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra etc. The international customers of the company include Bosch, Delphi, IKA, Borg Automotive etc. 30% of the products manufactured by the company are exported worldwide.
Future outlook:
The future outlook for the company manufacturing electrical components for automobiles appears promising, supported by strong industry growth drivers and favorable government policies. The increasing sales of new vehicles in India, both through physical dealerships and e-commerce platforms, along with the rise of multiple used vehicle sales platforms, is expanding market opportunities. The automotive sector is witnessing significant investments from global automobile giants, indicating long-term industry expansion. Furthermore, the Indian government’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, aims to strengthen manufacturing capabilities and exports, creating a favorable business environment. In a major boost to the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, the exemption of customs duty on the import of capital goods and machinery for lithium-ion cell production is expected to accelerate EV adoption, indirectly benefiting component manufacturers. Additionally, both Indian and global manufacturers are investing in new capacities and advanced programs to secure long-term advantages.
Areas of Concern:
A key challenge is the lack of adequately skilled labor, which affects productivity and the ability to meet evolving industry demands. Additionally, the low adoption of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) hampers process automation and digital transformation, limiting efficiency gains. Regulatory disruptions also pose a significant risk, as frequent changes in policies and compliance requirements can create operational uncertainties. Another critical concern is the semiconductor industry’s inability to fully support the rising demand for high-end passenger vehicle components. This supply constraint could hinder the company’s projected growth and affect industry forecasts by various organizations.
Dental Products Business:
There’s a growing awareness of the importance of oral health and its impact on overall health and well-being. This awareness has led to increased demand for dental services and products, as well as a focus on patient education and preventive care initiatives.
DPI is a pioneer in manufacture of dental products in India with a proven track record since 1962. The company exports its produce to over 15 countries worldwide. The company is also awarded CE mark for its manufactured product range for its quality and reliability. The company has a strong dealer network of over 100 dealers in India. The wide range of products manufactured by this division include files, dental burs, restorative materials, impression material, endodontic material etc.
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for the company manufacturing dental and oral hygiene products is positive, driven by increasing disposable incomes in India, which are enabling more people to opt for dental treatments beyond basic oral care. The rising number of dental clinics and practices is contributing to a growing demand for high-quality dental supplies, including consumables, instruments, and materials, presenting significant market opportunities.
Areas of Concern:
The industry is highly competitive, with both domestic and international players striving to capture market share. This intense competition could lead to pricing pressures and reduced profit margins, making it crucial for companies to focus on product quality, innovation, and efficient distribution to maintain a competitive edge in the evolving dental care sector.
****************************************************
Quantitative Analysis
Leverage Ratios

Observations:
- The company has managed to reduce its debt levels during this period. In absolute terms the debt has reduced by 7.69% however, there is increase in shareholder’s equity which has led to far greater reduction in ratio.
Operating Ratios

Observations:
- The company has maintained a positive working capital during the period indicating that its current assets are sufficient to cover its current liabilities.
- Receivable turnover has remained fairly stable during the period.
Profitability Ratios

Observations:
- During the period the company has worked with an average PAT margin of 5.05%.
- The company has given an average return on capital of 7.61% during the period, however, at current enterprise valuation the return works out to be almost equal to long term Government of India Bond Coupons for a new investor.
****************************************************
To learn Fundamental Analysis and
Company Intrinsic Valuation
Visit
Intrinsic Analyst – Learning Center.
Also Check out Testimonials of people who joined us in this Investment Journey!!!
****************************************************
Author
Jibu Dharmapalan
SEBI Registered Research Analyst
Registration No. INH000014678
GSTIN: 32AHVPD3247L2Z3
Mobile: +91 9656125475
Click Here To Contact on – Whatsapp or Telegram
Check Intermediary on SEBI Website
If You Like This Content 👇👇👇
Click Here To Join Us on Facebook For Free Live Interactive Discussion And Learning
References:
BSE India – BBTC Ltd. Annual Reports
BBTC Ltd. – Investors – Annual Reports
Click Here for Home
FAQs
What is Intrinsic Value?
Ans: When someone invests in an asset, he does so in order to earn money from the business. The investor gets paid over a period of time as long as he is invested in the asset. Now intrinsic value is the present value of all such future cash flows generated by the asset. So logically one should not invest in any asset if the ask price is more than the intrinsic value of the asset.
How is Intrinsic Value of a company calculated?
Ans: For calculating the intrinsic value of a company all its future cash flows are extrapolated based on the past performance of the company, assumptions about the future growth of the company and its terminal value. Once all these are calculated these are brought to the present date based on appropriate discounting rate. The sum of all these gives the intrinsic value of the company. It may be more or less than the market capitalization of the company. If it is more than the market capitalization of the company then the company is said to be undervalued and is a good bet as a long-term investment and vice versa.
How is Intrinsic Value of a share calculated?
Ans: Once intrinsic value of a company is calculated as explained above, it is divided by the total number of outstanding shares of the company. This gives the intrinsic value of a share.
What is Discounted Cash Flow?
Ans: When we have cash flows that are spread over a period of time then Discounted Cash Flow method is used to calculate present value of all such cash flows. The present value depends on the discounting rate used. Usually 10 year Government bond yield rate(risk free rate of return) is used as the discounting rate.
















