
GNFC Ltd. – Stock Analysis (2024-25)
In this article we will try to analyze GNFC Ltd. based on previous six years of financial statements viz Balance sheet, Profit and Loss statement and Cash flow statement. With this fundamental analysis we will try to gain insight into the business activities, financial health, operating efficiency and profitability of the company and finally try to derive the intrinsic value of the stock using Discounted Cash Flow method and the price at which the stock becomes attractive for long term investment. This article is divided in three sections as listed below :-
Section 1: Qualitative Fundamental Analysis comprising of General Introduction, Business overview dwelling into Business Model, Strengths and Weakness, Long Term Sustainability and finally the competitors.
Section 2:Quantitative Fundamental Analysis on Financial Health, Operating Efficiency And Profitability.
Section 3: Calculation Of Intrinsic Value.
General Introduction
Dated: 18 Apr 25
Company: GNFC Ltd.
CMP: Rs. 507.00
Market Capitalisation: Rs. 7,449.89 Cr.
Share Holding Pattern:
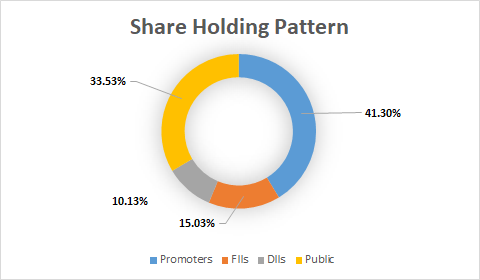
Promoters: Government of India
Peers: Pidilite Industries, SRF, Deepak Nitrite
Fundamental Analysis Of GNFC Ltd.
Qualitative Analysis
General Introduction:
It is a company with more than four decades of experience in the field of fertilizers. It is a joint enterprise promoted by Government of Gujarat and Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd. Starting with ammonia, urea, methanol and formic acid, Over the years the company has extended its profile much beyond fertilizers through a process of horizontal integration to chemicals, petrochemicals, energy, electronics and Information Technology.
Business Overview:
The company operates three verticals viz. Fertilizers, Chemicals and Information Technology, with Fertilizers and Chemicals being the mainstay.
- Fertilizer Segment
- Chemical Segment
- Information Technology
Most of company’s products are competing with big multinational players at import parity. Since India is net importer of oil and gas and this being primary feed/fuel for company, its financial performance is dependent upon how these variables play out.
Fertilizer Segment:
The production and sale of fertilizers commenced with the creation of one of the biggest single stream ammonia, urea facilities. This operation encompasses, the production of urea and ammonia, nitro phosphate, which are sold under the brand name, Narmada.
One of the key challenges that has emerged recently is the change in revenue realization post implementation of DBT scheme. The Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) scheme for fertilizers has been implemented throughout the country from March 2018. This scheme has changed the business model for fertilizers companies. Subsidy under the scheme becomes due only on sale of fertilizers by the retailers to the farmers through POS (Point of Sales) machines.
Earlier 90 % and 95% of the subsidy amount of Nitro phosphate and Urea respectively was getting paid on receipt of fertilizers at the field warehouse / retailers. This has postponed the payment of subsidy by about of six months as per the report of Fertilizer Association of India. This is because dispatches are continuous during the year but sales of fertilizers are seasonal. Hence, DBT has further increased the requirement of working capital in general.
The other challenge faced by the fertilizer industry is that, in India farming is heavily dependent on monsoons. Unlike many other countries where short fall in a rainfall is overcome through better irrigation facilities, India still needs to improve upon its Irrigation infrastructure to reduce a dependency on monsoons. Though there are many such projects that are envisaged, most of them are still in planning phase.
Chemical Segment:
The company operates, one core, chemical and petrol chemical plants, producing methanol, formic acid, Tolune Di-isocyanate, technical grade urea, weak, nitric acid, anile, concentrated nitric acid, acetic acid, ethyl, acetate, and ammonium nitrate. GNC is the sole producer of acetic acid and one of two producers of formic acid in India. It was the largest single streamline plant in India, and is the only manufacturer of Tolune Di-isocyanate in Southeast Asia and Indian subcontinent.
India is one of the world’s leading chemical producers and exporters. India is the sixth largest producer of chemicals and the fourth largest producer of agro-chemicals globally. The Indian Chemicals Industry is one of the most diversified among other industrial sectors covering a multitude of commercial products and comprises of both small scale as well as large scale units. It fuels the needs of several downstream industries such as textiles, papers, paints, varnishes, soaps, detergents, pharmaceuticals, etc. With linkages to several other sectors of the economy, it enjoys a position of paramount importance. The rapid expansion of the various sub-sectors like bulk, specialty, petrochemicals, agro-chemicals, fertilizers, etc., can be attributed to favorable government policies growing demand from multiple end-user sectors, the growing domestic customer base and changes in consumers’ lifestyles.
To facilitate the indigenous production of chemicals, the Government of India has allowed 100 per cent FDI in the chemicals sector. The production of most chemicals, including organic/inorganic products, dyes, and pesticides, has been de-licensed to allow ease of doing business in the segment.
Information Technology:
GNC’s IT division, (n)Code Solutions, has launched a top-tier PKI facility to provide digital signature certificates and various PKI-based solutions. These certificates can integrate with the application like emails, workflow enterprise systems, or secure VPNs, and are used by individuals, corporations, and governments to secure online transactions. Additionally, (n)Code Solutions offer value, added IT services, such as system integration, Smart, city, implementation, e-auction, e-procurement, Blockchain and cloud services.
Revenue Breakup:
| 2021-22 | 2023-24 | |
| Fertilizers | 29.03 | 38% |
| Chemicals | 69.95 | 60% |
| Information Technology | 1.02 | 2% |
Given the above we can conclude that in future, the three verticals in which the company operates are very likely to see the benefits of increasing population, growth in other industries like textiles, paints, household chemicals etc. and support from government policies like Atmanirbhar Bharat.
****************************************************
Quantitative Analysis
Leverage Ratios

Observations:
- The company has almost no debt.
- Due to the extremely low debt levels the company is successful in maintaining a healthy interest coverage ratio during the period in consideration.
Operating Ratios
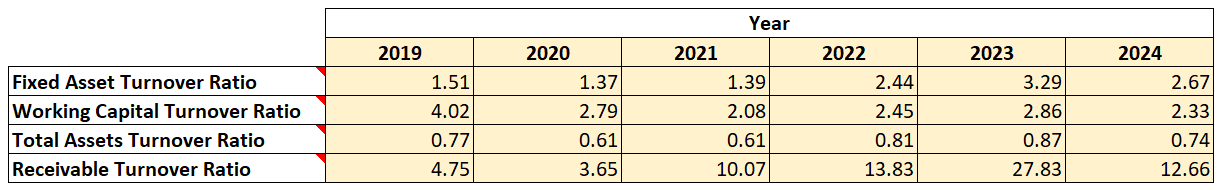
Observations:
- The company has maintained a positive working capital turnover ratio, indicating that its current assets are sufficient to cover its current liabilities. However, there is a decrease in this ratio indicating that the efficiency with which the company was utilizing its working capital has come down during the period.
- The receivable turnover ratio has improved during the period, indicating that the company is proactive in collecting the dues from the market.
Profitability Ratios
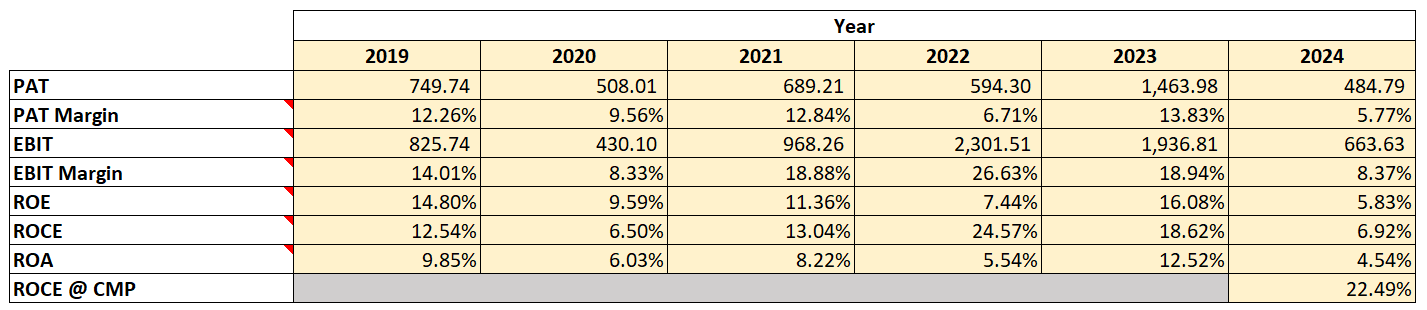
Observations:
- There has been a decrease in the PAT in 2024 as compared to the previous years, however, the company has maintained a good PAT margin of 10.16% during this period indicating its pricing power in the sectors it serves.
- The average ROCE of the company during the period has been 13.70%. For a new investor ROCE has to be worked out based on the Enterprise value, and this works out to be 22.49% which is better than long term Government of India Bond Coupons.
****************************************************
To learn Fundamental Analysis and
Company Intrinsic Valuation
Visit
Intrinsic Analyst – Learning Center.
Also Check out Testimonials of people who joined us in this Investment Journey!!!
****************************************************
Author
Jibu Dharmapalan
SEBI Registered Research Analyst
Registration No. INH000014678
GSTIN: 32AHVPD3247L2Z3
Mobile: +91 9656125475
Click Here To Contact on – Whatsapp or Telegram
Check Intermediary on SEBI Website
If You Like This Content 👇👇👇
Click Here To Join Us on Facebook For Free Live Interactive Discussion And Learning
References:
BSE India – GNFC Ltd. Annual Reports
GNFC Ltd. – Investors – Annual Reports
Click Here for Home
FAQs
What is Intrinsic Value?
Ans: When someone invests in an asset, he does so in order to earn money from the business. The investor gets paid over a period of time as long as he is invested in the asset. Now intrinsic value is the present value of all such future cash flows generated by the asset. So logically one should not invest in any asset if the ask price is more than the intrinsic value of the asset.
How is Intrinsic Value of a company calculated?
Ans: For calculating the intrinsic value of a company all its future cash flows are extrapolated based on the past performance of the company, assumptions about the future growth of the company and its terminal value. Once all these are calculated these are brought to the present date based on appropriate discounting rate. The sum of all these gives the intrinsic value of the company. It may be more or less than the market capitalization of the company. If it is more than the market capitalization of the company then the company is said to be undervalued and is a good bet as a long-term investment and vice versa.
How is Intrinsic Value of a share calculated?
Ans: Once intrinsic value of a company is calculated as explained above, it is divided by the total number of outstanding shares of the company. This gives the intrinsic value of a share.
What is Discounted Cash Flow?
Ans: When we have cash flows that are spread over a period of time then Discounted Cash Flow method is used to calculate present value of all such cash flows. The present value depends on the discounting rate used. Usually 10 year Government bond yield rate(risk free rate of return) is used as the discounting rate.
















